- Home
- Resources
- Work samples
- Samples
- Water in the world - ABOVE
Humanities and Social Sciences
Year 7
Above satisfactory
Data analysis: Water in the world
Summary of task
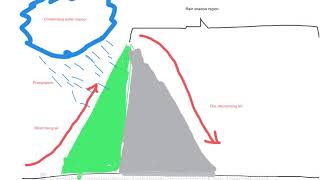
Students explored how water connects places, environments and people. Provided with images, graphs and thematic world maps showing average annual precipitation and access to improved drinking water, students were asked to identify global patterns of average precipitation and access to improved drinking water; describe the relationships between these patterns; and provide reasons for the identified relationships. Students used digital technologies to present the process of orographic rainfall and explain how it influences the characteristics on either side of a mountain. They evaluated the use of maps to understand the limitation of information, and concluded their studies by evaluating the sustainability of alternative strategies for water management. These activities were completed in class over a period of six weeks.
Achievement standard
By the end of Year 7, students explain the role of groups and the significance of particular individuals in past societies. They suggest reasons for continuity and change over time. They describe the effects of change on societies, individuals and groups and describe events and developments from the perspective of people who lived at the time. They identify past events and developments that have been interpreted in different ways. Students describe geographical processes that influence the characteristics of places. They explain interconnections between people and places and people and environments, describing how these interconnections change places and environments. Students identify the ideas, values and principles that underpin the institutions and processes in Australia’s political and legal systems. They explain the diverse nature of Australian society, and identify the importance of shared values in contemporary Australian society. Students describe the interdependence of consumers and producers in the market and identify factors and strategies that contribute to the financial success of businesses and individuals. They identify why individuals choose to work and the various sources of income that exist. Students recognise that people have different perceptions of places, events and issues and explain how this and other factors influence views on how to respond to an issue or challenge.
Students formulate significant questions and propositions to guide investigations. They locate and collect useful data, information and evidence from a range of primary and secondary sources. They examine sources to determine their origin, purpose and reliability and to identify past and present values and perspectives. They interpret and analyse data to propose simple explanations for distributions, patterns, trends and relationships, and evaluate and synthesise evidence to draw conclusions. Students sequence events and developments within a chronological framework, using dating conventions to represent and measure time. They organise, categorise and represent data in a range of appropriate formats using discipline-specific conventions. They make informed decisions by collaborating with others to generate alternatives, comparing the potential costs and benefits of each and developing and using criteria to make a reasoned judgement. Students reflect on their learning to propose individual and collective action in response to an issue or challenge, taking account of different factors and multiple perspectives, and predict the probable effects of their proposal. They present ideas, findings, viewpoints, explanations and conclusions in a range of communication forms that incorporate source materials, citations, discipline-specific terms, conventions and concepts.
By the end of Year 7, students describe geographical processes that influence the characteristics of places and how characteristics of places are perceived and valued differently. They explain interconnections between people and places and people and environments and describe how these interconnections change places and environments. They describe alternative strategies for a geographical challenge, referring to environmental, economic and social factors involved.
Students develop geographically significant questions to frame and guide an inquiry process. They locate, collect, organise and categorise useful data and information from a range of primary and secondary sources. They record and represent data and the location and distribution of geographical phenomena in a range of graphic forms, including large-scale and small-scale maps that conform to cartographic conventions. They analyse geographical data and other information to propose simple explanations for spatial patterns, trends and relationships, and draw conclusions. Students present findings and arguments using relevant geographical terminology, digital technologies and graphic representations in a range of communication forms. They propose action in response to a geographical challenge, taking account of environmental, economic and social factors, and describe the expected effects of their proposal.
 1
Learning Area
1
Learning Area
Articulates the overall connection between water, people, places and environments 2 Subject - Geography
Articulates the overall connection between water, people, places and environments 3 Learning Area
Explains a connection between people’s use of water and its impact on the environment 4 Subject - Geography
Explains a connection between people’s use of water and its impact on the environment 5 Learning Area
Predicts a geographical outcome using a conceptual argument 6 Subject - Geography
Predicts a geographical outcome using a conceptual argument
-
Annotations
-
1
Learning Area
Articulates the overall connection between water, people, places and environments -
2
Subject - Geography
Articulates the overall connection between water, people, places and environments -
3
Learning Area
Explains a connection between people’s use of water and its impact on the environment -
4
Subject - Geography
Explains a connection between people’s use of water and its impact on the environment -
5
Learning Area
Predicts a geographical outcome using a conceptual argument -
6
Subject - Geography
Predicts a geographical outcome using a conceptual argument
 1
Learning Area
1
Learning Area
Provides a comprehensive description of how interconnections change places and environments 2 Subject - Geography
Provides a comprehensive description of how interconnections change places and environments 3 Learning Area
Uses relevant geographical terminology in an appropriate context 4 Subject - Geography
Uses relevant geographical terminology in an appropriate context 5 Learning Area
Draws conclusions using multiple connections from the diagram 6 Subject - Geography
Draws conclusions using multiple connections from the diagram 7 Learning Area
Describes in detail the interconnections between people’s actions and the environment 8 Subject - Geography
Describes in detail the interconnections between people’s actions and the environment
-
Annotations
-
1
Learning Area
Provides a comprehensive description of how interconnections change places and environments -
2
Subject - Geography
Provides a comprehensive description of how interconnections change places and environments -
3
Learning Area
Uses relevant geographical terminology in an appropriate context -
4
Subject - Geography
Uses relevant geographical terminology in an appropriate context -
5
Learning Area
Draws conclusions using multiple connections from the diagram -
6
Subject - Geography
Draws conclusions using multiple connections from the diagram -
7
Learning Area
Describes in detail the interconnections between people’s actions and the environment -
8
Subject - Geography
Describes in detail the interconnections between people’s actions and the environment
 1
Learning Area
1
Learning Area
Presents an argument about a geographical phenomenon 2 Subject - Geography
Presents an argument about a geographical phenomenon 3 Learning Area
Describes a reason why people may perceive and value water differently 4 Subject - Geography
Describes a reason why people may perceive and value water differently 5 Learning Area
Explains the challenges associated with multiple uses of a single body of water 6 Subject - Geography
Explains the challenges associated with multiple uses of a single body of water 7 Learning Area
Proposes an explanation for negative use of water 8 Subject - Geography
Proposes an explanation for negative use of water 9 Learning Area
Synthesises evidence from multiple sources 10 Subject - Geography
Synthesises evidence from multiple sources 11 Learning Area
Draws a conclusion about how people view water differently 12 Subject - Geography
Draws a conclusion about how people view water differently
-
Annotations
-
1
Learning Area
Presents an argument about a geographical phenomenon -
2
Subject - Geography
Presents an argument about a geographical phenomenon -
3
Learning Area
Describes a reason why people may perceive and value water differently -
4
Subject - Geography
Describes a reason why people may perceive and value water differently -
5
Learning Area
Explains the challenges associated with multiple uses of a single body of water -
6
Subject - Geography
Explains the challenges associated with multiple uses of a single body of water -
7
Learning Area
Proposes an explanation for negative use of water -
8
Subject - Geography
Proposes an explanation for negative use of water -
9
Learning Area
Synthesises evidence from multiple sources -
10
Subject - Geography
Synthesises evidence from multiple sources -
11
Learning Area
Draws a conclusion about how people view water differently -
12
Subject - Geography
Draws a conclusion about how people view water differently
 1
Learning Area
1
Learning Area
Describes accurately a geographic trend, citing specific data from the graph 2 Subject - Geography
Describes accurately a geographic trend, citing specific data from the graph 3 Learning Area
Identifies relationships between variables 4 Subject - Geography
Identifies relationships between variables 5 Learning Area
Uses relevant geographical terminology 6 Subject - Geography
Uses relevant geographical terminology 7 Learning Area
Synthesises data to draw a detailed conclusion 8 Subject - Geography
Synthesises data to draw a detailed conclusion 9 Learning Area
Explains how access to safe drinking water is connected to life expectancy, citing examples from the graph 10 Subject - Geography
Explains how access to safe drinking water is connected to life expectancy, citing examples from the graph
-
Annotations
-
1
Learning Area
Describes accurately a geographic trend, citing specific data from the graph -
2
Subject - Geography
Describes accurately a geographic trend, citing specific data from the graph -
3
Learning Area
Identifies relationships between variables -
4
Subject - Geography
Identifies relationships between variables -
5
Learning Area
Uses relevant geographical terminology -
6
Subject - Geography
Uses relevant geographical terminology -
7
Learning Area
Synthesises data to draw a detailed conclusion -
8
Subject - Geography
Synthesises data to draw a detailed conclusion -
9
Learning Area
Explains how access to safe drinking water is connected to life expectancy, citing examples from the graph -
10
Subject - Geography
Explains how access to safe drinking water is connected to life expectancy, citing examples from the graph
 1
Learning Area
1
Learning Area
Uses relevant geographical terminology 2 Subject - Geography
Uses relevant geographical terminology 3 Learning Area
Draws a reasoned, detailed conclusion based on the data provided in the graph, using examples 4 Subject - Geography
Draws a reasoned, detailed conclusion based on the data provided in the graph, using examples
-
Annotations
-
1
Learning Area
Uses relevant geographical terminology -
2
Subject - Geography
Uses relevant geographical terminology -
3
Learning Area
Draws a reasoned, detailed conclusion based on the data provided in the graph, using examples -
4
Subject - Geography
Draws a reasoned, detailed conclusion based on the data provided in the graph, using examples
 1
Learning Area
1
Learning Area
Identifies the purpose of different maps 2 Subject - Geography
Identifies the purpose of different maps 3 Learning Area
Justifies the need for more information by acknowledging each map’s limitations 4 Subject - Geography
Justifies the need for more information by acknowledging each map’s limitations 5 Learning Area
Uses both maps to explain in detail trends and relationships about rainfall and population 6 Subject - Geography
Uses both maps to explain in detail trends and relationships about rainfall and population
-
Annotations
-
1
Learning Area
Identifies the purpose of different maps -
2
Subject - Geography
Identifies the purpose of different maps -
3
Learning Area
Justifies the need for more information by acknowledging each map’s limitations -
4
Subject - Geography
Justifies the need for more information by acknowledging each map’s limitations -
5
Learning Area
Uses both maps to explain in detail trends and relationships about rainfall and population -
6
Subject - Geography
Uses both maps to explain in detail trends and relationships about rainfall and population
 1
Learning Area
1
Learning Area
Identifies strategies to address the challenge of water sustainability 2 Subject - Geography
Identifies strategies to address the challenge of water sustainability 3 Learning Area
Explains in detail the processes of water recycling and desalination 4 Subject - Geography
Explains in detail the processes of water recycling and desalination 5 Learning Area
Identifies possible positive and negative social and economic factors linked to recycled water and desalination 6 Subject - Geography
Identifies possible positive and negative social and economic factors linked to recycled water and desalination 7 Learning Area
Connects sustainable strategies for water to society and the environment 8 Subject - Geography
Connects sustainable strategies for water to society and the environment 9 Learning Area
Outlines positive and negative economic impacts associated with water recycling and desalination, using examples 10 Subject - Geography
Outlines positive and negative economic impacts associated with water recycling and desalination, using examples 11 Learning Area
Identifies and explains a connection between desalination, the economy and the environment 12 Subject - Geography
Identifies and explains a connection between desalination, the economy and the environment 13 Learning Area
Explains economic advantages and disadvantages of water recycling and desalination on society and the economy, using specific examples 14 Subject - Geography
Explains economic advantages and disadvantages of water recycling and desalination on society and the economy, using specific examples 15 Learning Area
Draws conclusions about the effects of water recycling and desalination 16 Subject - Geography
Draws conclusions about the effects of water recycling and desalination
-
Annotations
-
1
Learning Area
Identifies strategies to address the challenge of water sustainability -
2
Subject - Geography
Identifies strategies to address the challenge of water sustainability -
3
Learning Area
Explains in detail the processes of water recycling and desalination -
4
Subject - Geography
Explains in detail the processes of water recycling and desalination -
5
Learning Area
Identifies possible positive and negative social and economic factors linked to recycled water and desalination -
6
Subject - Geography
Identifies possible positive and negative social and economic factors linked to recycled water and desalination -
7
Learning Area
Connects sustainable strategies for water to society and the environment -
8
Subject - Geography
Connects sustainable strategies for water to society and the environment -
9
Learning Area
Outlines positive and negative economic impacts associated with water recycling and desalination, using examples -
10
Subject - Geography
Outlines positive and negative economic impacts associated with water recycling and desalination, using examples -
11
Learning Area
Identifies and explains a connection between desalination, the economy and the environment -
12
Subject - Geography
Identifies and explains a connection between desalination, the economy and the environment -
13
Learning Area
Explains economic advantages and disadvantages of water recycling and desalination on society and the economy, using specific examples -
14
Subject - Geography
Explains economic advantages and disadvantages of water recycling and desalination on society and the economy, using specific examples -
15
Learning Area
Draws conclusions about the effects of water recycling and desalination -
16
Subject - Geography
Draws conclusions about the effects of water recycling and desalination